 Transferring a website to a new web hosting provider might be a challenge, since the site ownercannot have a 100% clear picture of how the site will fit into the specifics of the new server before the DNS propagation is complete.
Transferring a website to a new web hosting provider might be a challenge, since the site ownercannot have a 100% clear picture of how the site will fit into the specifics of the new server before the DNS propagation is complete.
Luckily, there are a few tricks that can help users get a clear idea of how the newly transferred content will load from the new server after the DNS propagation has been completed.
1. Use the temporary host assigned to a hosting account
At signup, users are assigned a fully functioning temporary host, which they can use to preview their site. All they need to do is transfer their site contents to the host’s folder and then see how the site will load from the new location by using its URL.
They can find the host’s URL in the Welcome email and in the Hosted Domains section of the Web Hosting Control Panel.
NOTE: Temporary URLs are not recommended for previewing sites that use a strict URL configuration (including WordPress, PrestaShop, osCommerce, etc. sites), since they may force a URL rewrite that goes back to the original domain name, which may result in a redirection to your previous host, or in the site not displaying at all.
2. Use the local host of a computer
Users can preview their website with their own domain name before the DNS propagation has been completed by using their local computer’s HOSTS file.
With a simple HOSTS file tweak, their computer will resolve the site locally prior to looking up the domain’s DNS records.
Here is how to use your computer’s HOST file on the two common Operating Systems:
Windows OS
1. Find the HOSTS file. It’s usually located here:
– Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/Vista/7 – C:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
– Windows 95/98/Me – C:\windows\hosts
2. Make sure you make a backup of the file before changing it.
3. Open the file with any text editor. There will be two columns, the first one containing IP addresses (e.g.: 127.0.0.1) and the second one – related hostnames (e.g.: localhost).
4. Add a new line with the IP of the server where your domain is hosted and then add your domain.
For example:
116.0.0.1 localhost
60.45.92.163 example.com
60.45.92.163 www.example.com5. Save all changes.
6. Now restart any opened browser. When the browser opens again, enter your site’s address – it should load from its new location.
7. If the site does not open, you may have to flush the DNS cache. Go to Start, and then Run, then type “cmd” and hit enter.
Type the following: ipconfig /flushdns
8. Your website should now open without a problem.
Mac OS X
1. Open the Terminal app (it’s located in the Utilities folder in your Applications folder).
2. Create a backup copy of your existing hosts file with the following command:
sudo cp /private/etc/hosts /private/etc/hosts-orig3. Enter your user password.
4. Now, it’s time to edit the file. Enter the following command:
sudo vi /private/etc/hosts5. Enter your user password.
6. If you get a permission error, go to your “Help” menu, search for “root” and follow the instructions for “Enabling the root user.” When you are ready, go back to step 2.
7. You will see a file with contents similar to the following:
##
# Host Database
#
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
# when the system is booting. Do not change this entry.
##
116.0.0.1 localhost
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
fe80::1%lo0 localhost
8. Add your domain and IP address to the bottom of the list. Press “i” to enter the “Insert mode”. When you are done modifying the file, press “Esc” to exit the “Insert mode”. Type “:wq” to save the changes and quit.
For example:
# Host Database
#
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
# when the system is booting. Do not change this entry.
##
116.0.0.1 localhost
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
fe80::1%lo0 localhost
60.45.92.163 example.com
60.45.92.163 www.example.com
9. You may also need to grant yourself sudo privileges. In your “Help” menu, search for “root” and select the instructions for “Enabling the root user.” Follow these.
10. Now restart any opened browser. When the browser opens again, enter your site’s address – it should load from its new location.
11. If the site does not open, you may have to flush the DNS cache. To do that, type the following in the Terminal:
dscacheutil -flushcache12. Your website should now open without a problem.
3. Use our site transfer services
If you or your customers consider site transfer as being too much of a challenge, you can make use of our site transfer service, which is included for free with each hosting package.
Our technicians will need authorized access to your hosting account with your previous host so that they could transfer the files over to our platform. They will then test your site on our servers and will make sure it resolves flawlessly from the new location as soon as the DNS propagation has been completed.
All you will need to do on your end is update the domain’s nameservers in your domain management account.

 ICANN, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, has put into circulation a new transfer policy for generic domain names.
ICANN, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, has put into circulation a new transfer policy for generic domain names.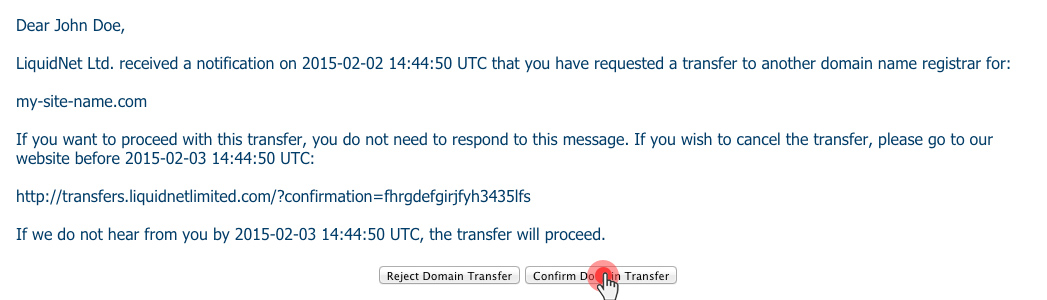
 In tune with the ever-shifting trends on the SSL market, we have moved to a more reasonably priced SSL provider and can now offer you a much more competitive pricing window for both generic and Wildcard SSL certificates.
In tune with the ever-shifting trends on the SSL market, we have moved to a more reasonably priced SSL provider and can now offer you a much more competitive pricing window for both generic and Wildcard SSL certificates.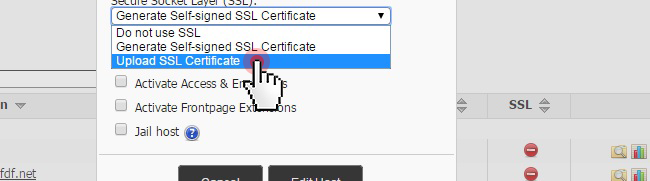
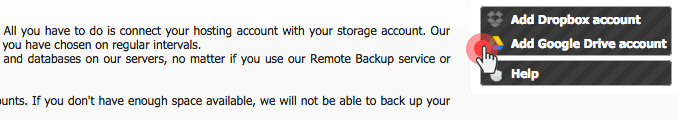
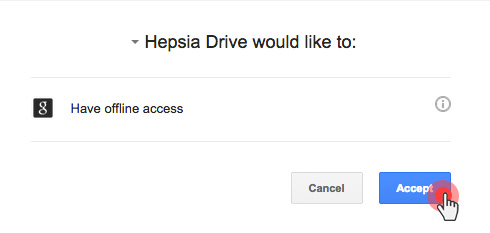
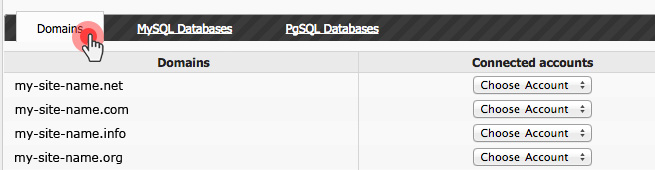
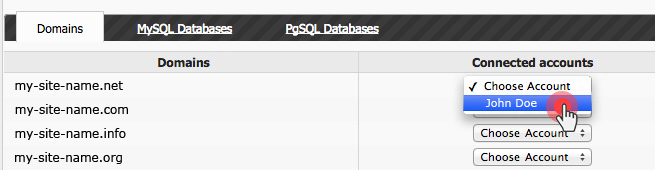
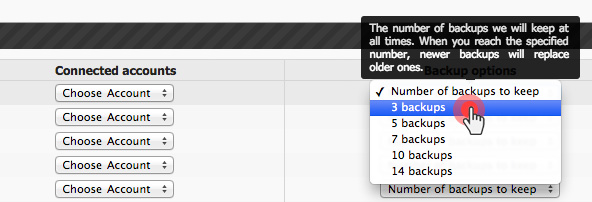
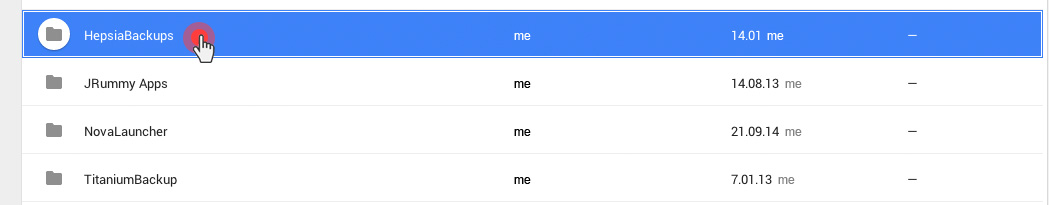
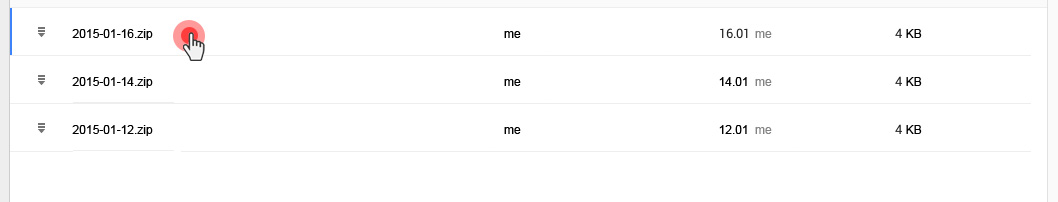
 Over the last year, we have improved the backup capabilities of our web hosting platform by enabling the option to back up your content to Dropbox and by making your data backups browsable and accessible with a click from the Web Hosting Control Panel.
Over the last year, we have improved the backup capabilities of our web hosting platform by enabling the option to back up your content to Dropbox and by making your data backups browsable and accessible with a click from the Web Hosting Control Panel.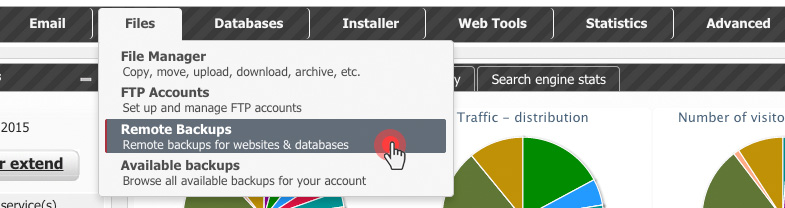
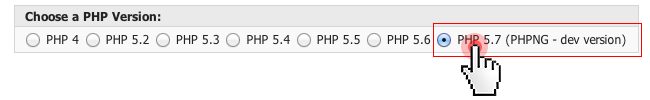
 PHP is a living language and as such, it undergoesconstant developments, experiments and upgrades. This is why, it is hard to predict how it will unfold within a year or even less.
PHP is a living language and as such, it undergoesconstant developments, experiments and upgrades. This is why, it is hard to predict how it will unfold within a year or even less.